Omdia View
Customers and consumers raised on the simplicity and predictability of digital-native commerce platforms, such as Amazon, Alibaba, and the like, expect the same joined-up and flawless experiences when interacting with any organization. Fragmented and product-centric organizations are unable to meet these rising customer expectations. They lack the organizational and systems coherence to sense customer intent and deliver a relevant in-context response.
Omnichannel customer engagement has been a top priority for several years, but progress has moved at a glacial pace. Back-office, supply, and logistics systems are often poorly connected to customer-facing systems, making it difficult for customers to know the status of products ordered or services consumed. The long-awaited 360-degree view of the customer has remained elusive (until now). It is usually limited to basic and transactional data that reveals little about the customer and their wants, needs, or behaviors. Fragmented data, systems, channels, and organizational silos prevent the oft-promised seamless experience now expected by customers.
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, transforming the customer experience was considered the lowest digital transformation priority out of nine initiatives monitored by Omdia. The Omdia ICT Enterprise Insights global survey (completed and published in September 2020) revealed a dramatic shift in importance; transforming the customer experience moved to the top of digital transformation priorities. 75% of enterprises consider customer experience more important since the COVID-19 lockdown. An analysis of customer-focused digital transformation over the last three years finds that in 2020 38% have made substantial progress, up 10% on the previous year. This, however, still means that 62% of enterprises are at risk of alienating their customers by not delivering insightful and relevant experiences.
CEPs provide a faster route to an omnichannel capability, especially when connected with operational systems to close the loop on brand promises and give customers much greater control. CEPs can be developed independently by enterprises by integrating existing technologies with the missing pieces from a wide variety of vendors. However, enterprises that have adopted this approach then have the ongoing challenge of incorporating updates from vendors whose applications have been developed on different code bases.
In this report, the vendors have either already done that integration work, integrating various acquisitions as they build their CEPs, or developed the entire platform on a common code base. Either way, by adopting a CEP suited to the business’s scale and industry requirements, enterprises can accelerate their abilities to sense, respond, and adapt at the right speed to enhance their customer relevance. That is the faster route back to growth post-COVID-19.
Key Messages
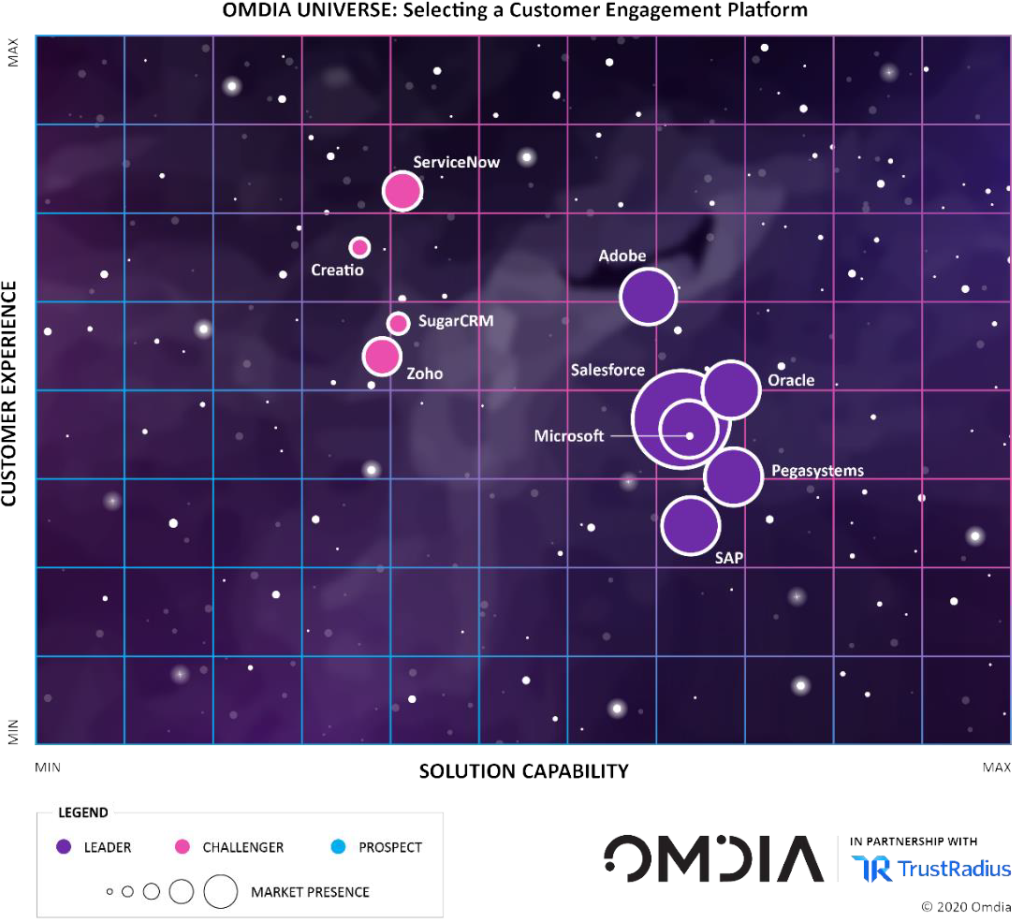
- The value of a CEP is more than the sum of its individual functional parts. To reflect this, additional weightings were applied to experience orchestration, AI and automation, and customer data management.
- A cluster of leaders have made substantial progress in delivering a unified enterprise CEP. These are Adobe, Microsoft, Oracle, Pegasystems, Salesforce, and SAP.
- Oracle and Pegasystems share the number one spot with the other leaders close behind.
- ServiceNow offers an alternative route to customer engagement through its platformof- platforms strategy, orchestrating enterprise workflows to deliver class-leading customer service.
- Among the challengers, Creatio, SugarCRM, and Zoho will appeal most to midmarket or larger B2B enterprises that seek greater simplicity allied to deeper customer insight.








